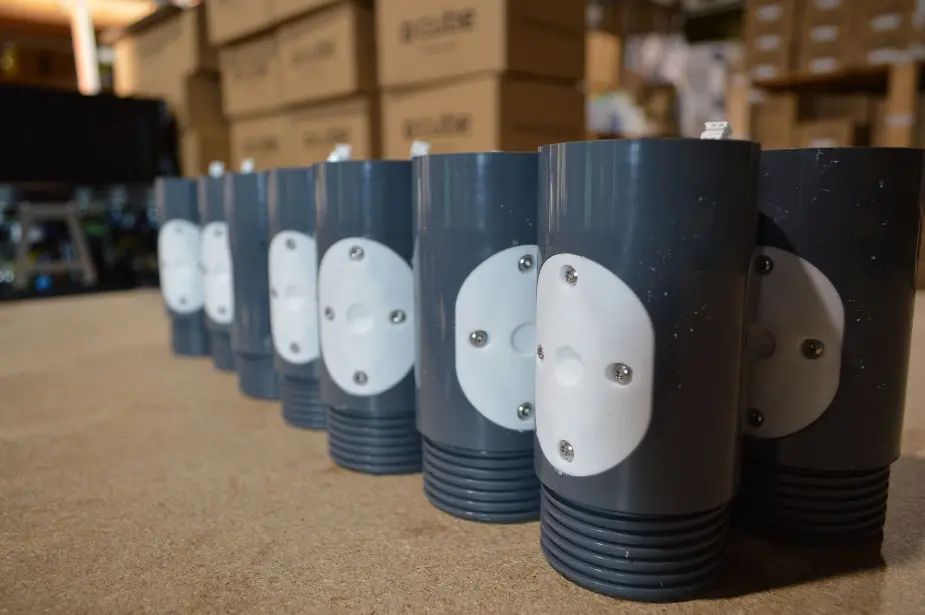
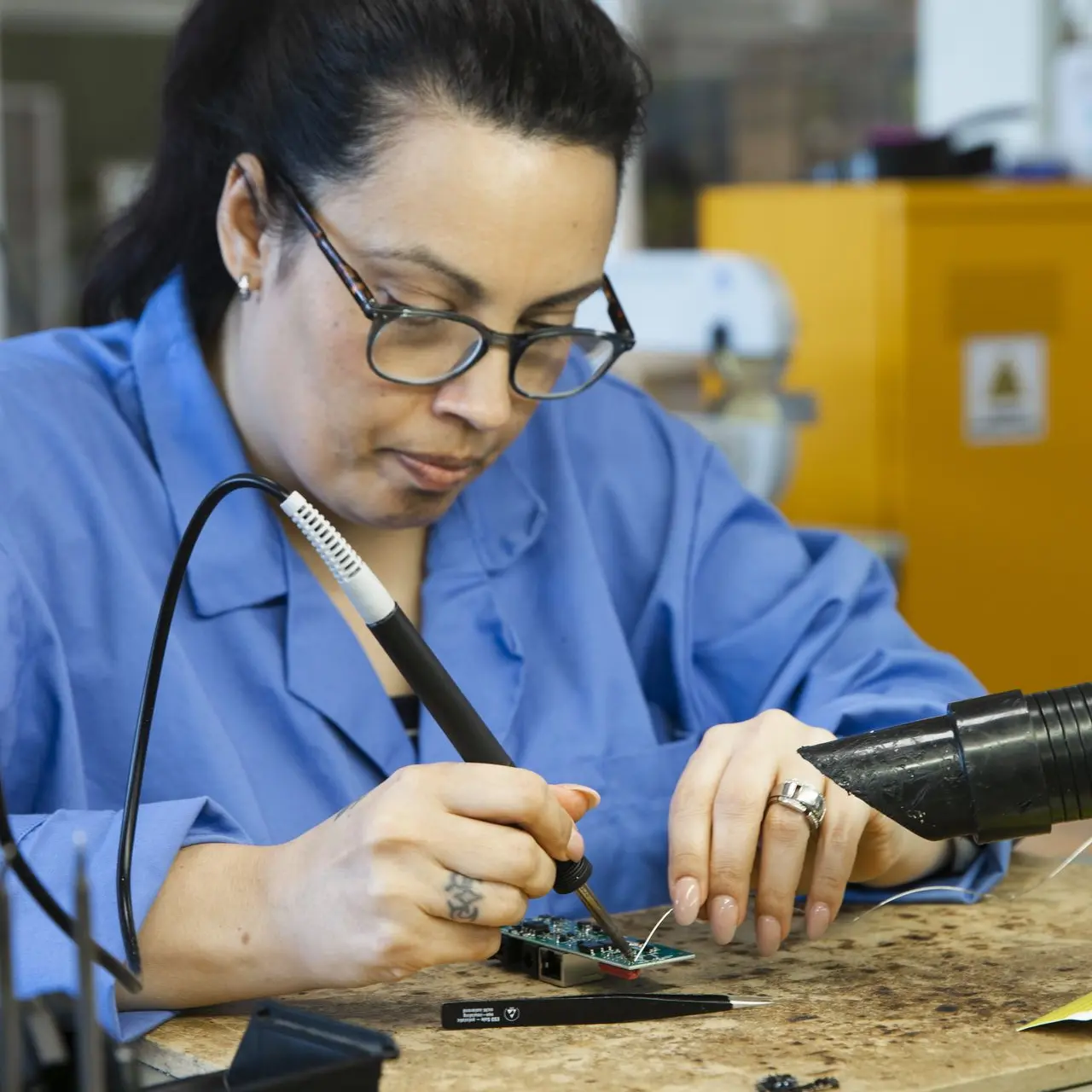
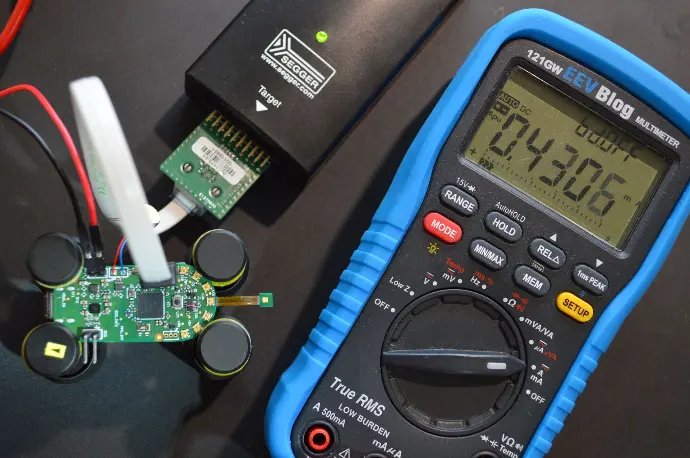
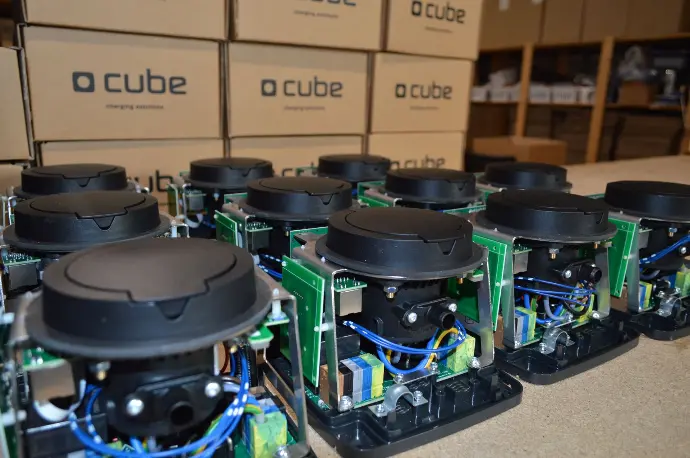
Prototyping balances innovation with practical constraints, paving the way for successful product development.
In the first phase(s) of electronic product development there is a high importance for prototyping. Early prototypes might be quite basic, focusing on core functionalities, while later ones will be closer to the final product, including appearance and user interface. Here’s why prototyping is essential and why multiple rounds are often necessary to achieve the final, optimal result.
- - Prototyping helps turn abstract ideas into tangible forms, allowing designers and engineers to validate the core concept. This process ensures that the product will meet the intended use cases and that the basic design is sound.
- - The first prototypes often reveal design flaws
or limitations that weren’t apparent during the conceptual phase. This goes for the hardware, as well for the software design. These might
include issues with component placement, thermal management, or user interface
elements. By identifying these problems early, costly mistakes in later stages
can be avoided.
- - Prototypes allow for real-world testing of the product's functionality. This includes checking how well the electronic circuits work, whether the software interacts correctly with the hardware, and if the product behaves as expected under different conditions.
- - Prototypes can be used to gather feedback from stakeholders, potential users, and clients. This feedback is invaluable for making informed decisions about design adjustments, feature additions, or simplifications.
- - Prototyping is inherently an iterative process. Each round of prototyping builds on the last, with refinements and improvements being made at each step. This iterative process helps in honing the product’s design to meet both functional and aesthetic requirements.